PSORIASIS is an autoimmune condition that causes itchiness and discomfort in your skin. Symptoms of psoriasis include thick areas of discoloured skin covered with scales. These thick, scaly areas are called plaques. Plaque psoriasis is the most common type.
There are several types of psoriasis, including.
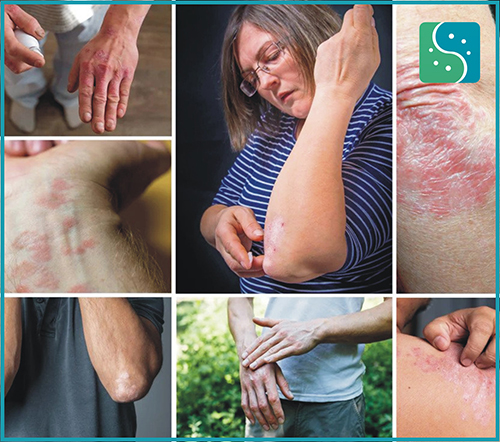
Psoriasis is an immune system disorder that results as a skin condition. Homoeopathy has the capacity to activate the body’s innate ability to heal itself and to rebuild the compromised immune system. Homoeopathic treatment target and combat the underlying cause of illness thereby restoring the distorted immunity. Homoeopathy offers long-lasting psoriasis treatment without any side effects.
The patient’s immune is strengthened by homoeopathic medicines, which improves the management of psoriasis. It also considers aggravating elements that can cause psoriasis flare-ups, such as infections and stress. Homoeopathic psoriasis treatment also slows the disease growth and lowers the risk of complications.
Symptoms of psoriasis on your skin include plaques. Plaques look like:
An early sign of psoriasis is small bumps. The bumps grow, and scales form on top. The surface of the plaque might shed, but the scales beneath them will stick together. If you scratch your rash, the scales may tear away from your skin. This can cause bleeding. As the rash continues to grow, lesions (larger areas of skin damage) can form. Symptoms of psoriasis can range from mild to severe.
In addition to skin plaques or a rash, symptoms might also include:
An over-reactive immune system that creates inflammation in your skin causes psoriasis. This creates inflammation or swelling, which you see on the surface of your skin as skin plaques.
It usually takes up to 30 days for new skin cells to grow and replace old skin cells. Your over-reactive immune system causes the timeline of new skin cell development to change to three to four days. The speed of new cells replacing old cells creates scales and frequent skin shedding on top of skin plaques.
Psoriasis runs in families. There may be a genetic component to psoriasis because biological parents may pass the condition down to their children.
An outbreak of psoriasis, or a flare up, causes symptoms of psoriasis as a result of contact with a trigger, which could be an irritant or an allergen. Psoriasis outbreaks differ from person to person. Common triggers for psoriasis flare ups include:
The doctor will diagnose psoriasis after a physical exam to look at your skin and review your symptoms.
The appearance of a skin plaque leads to a psoriasis diagnosis, but symptoms can relate to other similar skin conditions, so your doctor might offer a skin biopsy test to confirm your diagnosis.
No, psoriasis isn’t contagious. You can’t get psoriasis by coming into contact with another person’s psoriasis skin rash.
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that causes joint pain and swelling. Similar to psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis is an autoimmune condition that causes your immune system to function abnormally and cause symptoms. About 1 in 3 people diagnosed with psoriasis will also develop arthritis due to inflammation. Early treatment of psoriatic arthritis can reduce damage to your joints.
Psoriasis and eczema are two different skin conditions. Both conditions cause similar symptoms like discoloured skin, a rash and itching. Psoriasis plaques cause areas of thick skin covered in scales. Eczema causes a rash of dry and bumpy skin. Eczema also typically causes more intense itching than psoriasis.
To care your best with psoriasis.