The gallbladder is a pear-shaped pouch that sits just below the liver. It collects bile, a fluid made to help with digestion, as it flows from the liver to the intestine through the bile ducts.
Gallstones are deposits of digestive fluid made of solidified substances found in bile, like cholesterol. They are common and may or may not produce symptoms.
Homoeopathy is a system of medicine that uses natural substances to stimulate the body’s healing response. Homoeopathy is very effective in treating small sized gallbladder stones by reducing its size and dissolving the stones. Homoeopathic medicines are effective in alleviating pain as well as chronic inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis).
In cases of larger stones, multiple and impacted stones; homoeopathy has limited role to play and thus may need surgical intervention.
Homoeopathy also helps as preventive medicine in stone formation; preventing further stone production activity in the body. The best remedy for the patient is prescribed after taking note of the gall stone symptoms in each individual.
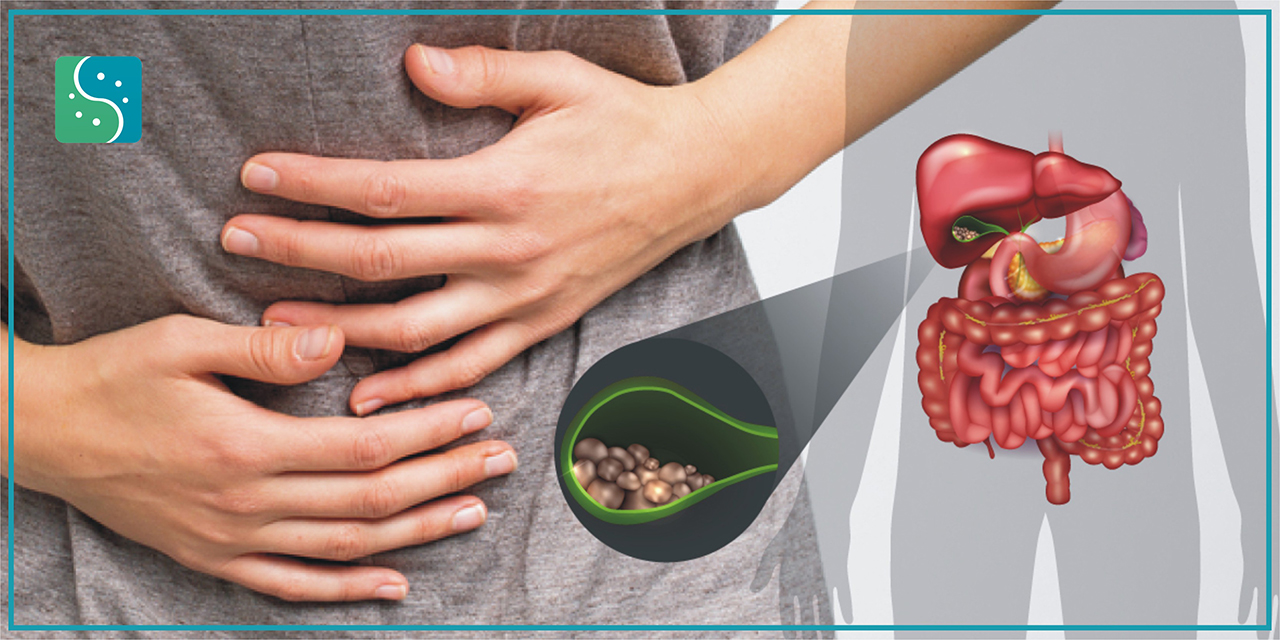
Gallstones are hardened deposits of bile that can form in your gallbladder. Bile is a digestive fluid produced in your liver and stored in your gallbladder. When you eat, your gallbladder contracts and empties bile into your small intestine (duodenum).
Gallstones range in size from as small as a grain of sand to as large as a golf ball. Some people develop just one gallstone, while others develop many gallstones at the same time.
Gallstones may cause no signs or symptoms. If a gallstone lodges in a duct and causes a blockage, the resulting signs and symptoms may include.
Gallstone pain may last several minutes to a few hours.
It's not clear what causes gallstones to form. Doctors think gallstones may result when.
Types of gallstones that can form in the gallbladder include.
COMPLICATIONS OF GALLSTONES may include.
A gallstone can cause a blockage in the pancreatic duct, which can lead to inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis). Pancreatitis causes intense, constant abdominal pain and usually requires hospitalization.
Gallbladder cancer. People with a history of gallstones have an increased risk of gallbladder cancer. But gallbladder cancer is very rare, so even though the risk of cancer is elevated, the likelihood of gallbladder cancer is still very small.
Your doctor will perform a physical examination that includes checking your eyes and skin for visible changes in colour. A yellowish tint may be a sign of jaundice, the result of too much bilirubin in your body.
The exam may involve using diagnostic tests that help your doctor see inside your body. These tests include:
To help improve your condition and reduce your risk of gallstones, try these tips.
If you plan to lose weight, do it slowly. Rapid weight loss may increase your risk of gallstones and other health problems.
While there is no medical documented way to completely prevent gallstones, cholesterol seems to play a major role in their formation. If you have a family history of gallstones, your doctor may advise you to limit foods with a high saturated fat content. Some of these foods include:
Because people living with obesity are more predisposed to gallstones, keeping your weight within a moderate range is another way to limit the possibility of their formation.
Gallstones are common, and most people will never be bothered by them. If they stay put in your gallbladder, you’ll probably never know they’re there. But once they begin to move, they become dangerous. These tiny, pebble-like pieces can do a lot of damage when they get into the tight spaces of your delicate biliary system.
A gallbladder attack can be intense and scary, especially if you didn’t know you had gallstones to begin with. Homoeopathic treatment is strongly recommended in cases of small sized stones to ease the pain and dissolving them. Homoeopathy also prevents further production of the stone in the body. For large or impacted stones, homoeopathy has limited role to play and thus you may need surgical intervention. Homoeopathic medicines are chosen after proper case taking and are based on the basis of principle of individualisation, thus always take medicines after consulting the homoeopathic doctor.